The best Solution to What Is Electric Cable
페이지 정보
작성자 Joie 작성일 25-09-11 10:14 조회 7 댓글 0본문
 Electric trams are environmentally pleasant, producing zero emissions during operation, which helps reduce urban air pollution and combat local weather change. Can you employ your GMPE bus move on Blackpool Trams? Along with this property, for wires and cables, there is one other property that determines how a lot present is allowed to move via a conductor. This property, referred to as ampacity (made from the two words "ampere" and "capacity"), defines the present capacity of a conductor primarily based on the heat that's generated owing to electrical present, the construction, and materials of the conductor, what is electric cable and ambient temperature. All conductors increase owing to heat generated in them when carrying present. Ampacity is determined based mostly on the heat generated in a conductor due to the present via it. It is easy to grasp, subsequently, that whereas the resistance of a wire will be virtually constant, its ampacity is determined by the temperature and another working situations, and it can't be a relentless. The unit of measurement for ρ, subsequently, is ohm-circular mil per foot (Ω.CM/ft).
Electric trams are environmentally pleasant, producing zero emissions during operation, which helps reduce urban air pollution and combat local weather change. Can you employ your GMPE bus move on Blackpool Trams? Along with this property, for wires and cables, there is one other property that determines how a lot present is allowed to move via a conductor. This property, referred to as ampacity (made from the two words "ampere" and "capacity"), defines the present capacity of a conductor primarily based on the heat that's generated owing to electrical present, the construction, and materials of the conductor, what is electric cable and ambient temperature. All conductors increase owing to heat generated in them when carrying present. Ampacity is determined based mostly on the heat generated in a conductor due to the present via it. It is easy to grasp, subsequently, that whereas the resistance of a wire will be virtually constant, its ampacity is determined by the temperature and another working situations, and it can't be a relentless. The unit of measurement for ρ, subsequently, is ohm-circular mil per foot (Ω.CM/ft).
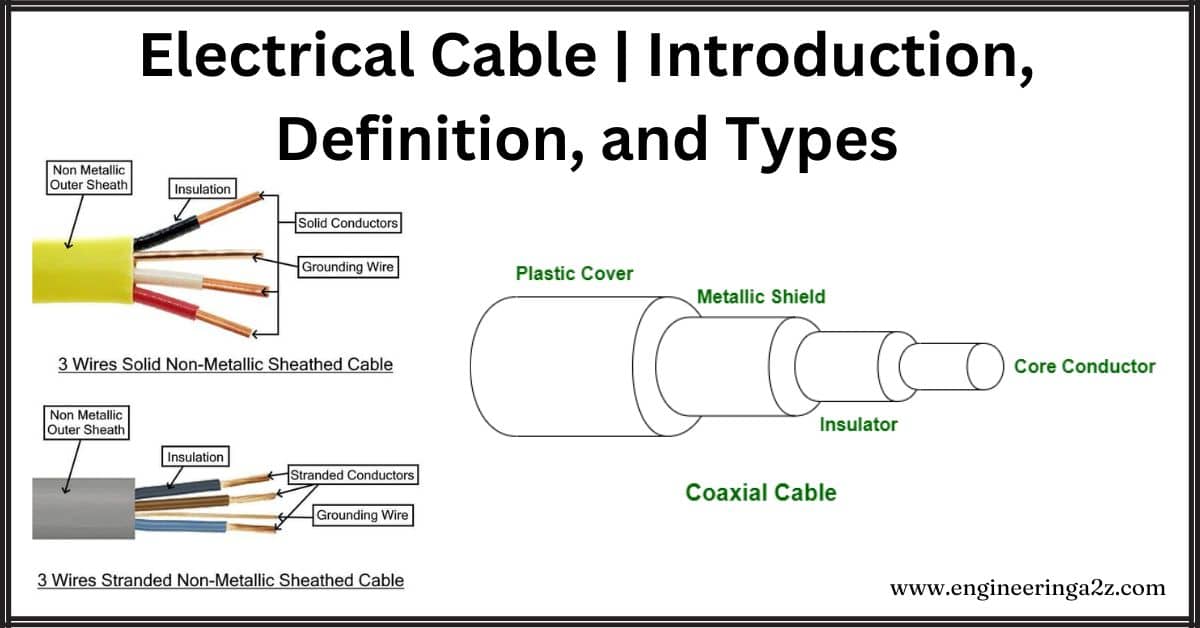 Therefore, this cable cannot carry such a high current. They are required on medium to high voltage techniques. A hole-type conductor consists of a core of excessive strength steel surrounded by a small gap crammed with temperature resistant grease. Stacked round this hole are the trapezoid shape stands of aluminum. In the seven-strand conductor, there are six aluminum strands round one steel cable. A CM is the area of a circle whose diameter is one mil (1/1000 of an inch). Knowing R permits one to determine voltage drop and the power transformed into heat in components of an electric circuit, in motor windings, and so forth. THWN is heat resistant and can be used at temperatures up to 167 °F or 75 °C. The duration a motor can withstand lock rotor current before it burns out varies primarily based on the motor's design and cooling methods. Theoretically, conductors may be made out of rigid bars.
Therefore, this cable cannot carry such a high current. They are required on medium to high voltage techniques. A hole-type conductor consists of a core of excessive strength steel surrounded by a small gap crammed with temperature resistant grease. Stacked round this hole are the trapezoid shape stands of aluminum. In the seven-strand conductor, there are six aluminum strands round one steel cable. A CM is the area of a circle whose diameter is one mil (1/1000 of an inch). Knowing R permits one to determine voltage drop and the power transformed into heat in components of an electric circuit, in motor windings, and so forth. THWN is heat resistant and can be used at temperatures up to 167 °F or 75 °C. The duration a motor can withstand lock rotor current before it burns out varies primarily based on the motor's design and cooling methods. Theoretically, conductors may be made out of rigid bars.
Conductors are both for overhead transmission traces or for underground installation. For transmission strains nowadays, the conductors are product of aluminum. This causes overhang conductors to sag more, which typically can lead to contacts with lower traces or bushes. Overhead conductors are naked wire and do not need insulation besides at residential areas where contact with timber and other objects is possible, whereas underground conductors can't be without insulation. This is very essential in areas where cables may be exposed to bodily hazards. There are numerous extra sorts of cables. There are other categories as nicely. The names are self-explanatory, to some extent, however can change from firm to company. Yes, the Hobart 5801 meat noticed can be equipped with a single part motor. Depending on the kind of termination, stress cones could either be constructed inside the pothead or molded over the original part. Also, to increase the conductivity of cables for the same cross-part, some cables have trapezoid shape strands that form circular layers, which resemble tubes of different diameters inside one another (see Figure 4). In this way, more use of house (thus, extra conductivity) is made out of the same conductor diameter. Figure 5 shows an image of such a cable.
Table 1 shows the precise resistance of some metals and nonmetals in the metric system. Table 1 also reveals the conductivity of supplies. Its unit within the metric system is, thus, 1/ohm-meter. Also proven within the desk is the temperature coefficient, which represents how a lot the particular resistance of a metal modifications with temperature. Temperature coefficient: Numerical worth (constructive for metals) representing how much the precise resistance of fabric changes with temperature. Where t2 is the temperature at which we have to know the particular resistance ρ2, t1 is the temperature at which the worth is understood (ρ1), α1 is the temperature coefficient at t1. Zero is the temperature coefficient at zero levels. It additionally explains key ideas comparable to resistance, ampacity, and specific resistance (resistivity), together with how these values vary with temperature and conductor design. The worth ρ is called the particular resistance or resistivity of a substance. Conductivity is the inverse of resistivity.
- 이전글 Drivers Licence Uk Tools To Make Your Daily Life Drivers Licence Uk Trick That Every Person Must Be Able To
- 다음글 Buy A Driver's License Legally Isn't As Tough As You Think
댓글목록 0
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.